The Waterpik Water Flosser: Significantly More Effective than Interdental Brush for Improving Gingival Health
Water Flosser compared to Interdental Brush on Bleeding Scores and Gingival Abrasion
Objective
To compare the effectiveness of a Waterpik Water Flosser (WF) and interdental brush (IDB) on bleeding indices and gingival abrasion.
Methodology
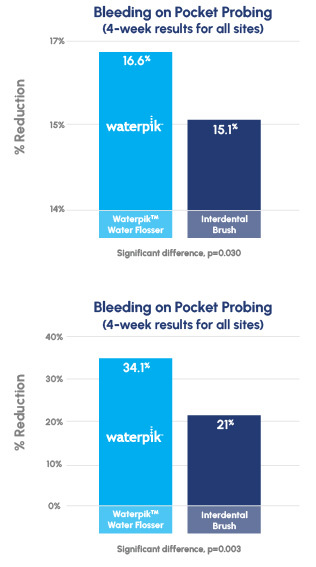
Seventy-eight subjects completed this 4-week, randomized controlled trial. Subjects were assigned to one of two groups; Waterpik Water Flosser (WF) plus a manual toothbrush or interdental brush (IDB) plus a manual toothbrush. Gingival inflammation was evaluated by measuring Bleeding on Pocket Probing (BOPP) and Bleeding on Marginal Probing (BOMP). Data was collected on contra-lateral quadrants. The Gingival Abrasion Score (GAS) was used to compare the incidence of abrasion between the groups.
Results
Both groups demonstrated a significant reduction in BOPP and BOMP from baseline to four weeks for all sites and interdental sites separately. The WF group was significantly more effective than the IDB group for reducing BOPP for all sites at week four (p=0.030) and BOMP for all sites and interdental sites at week four (p=0.003, p=0.019 respectively). There were no differences in gingival abrasion scores between the groups.
Conclusion
The Waterpik Water Flosser is significantly more effective than the interdental brush for improving gingival health in this clinical study.